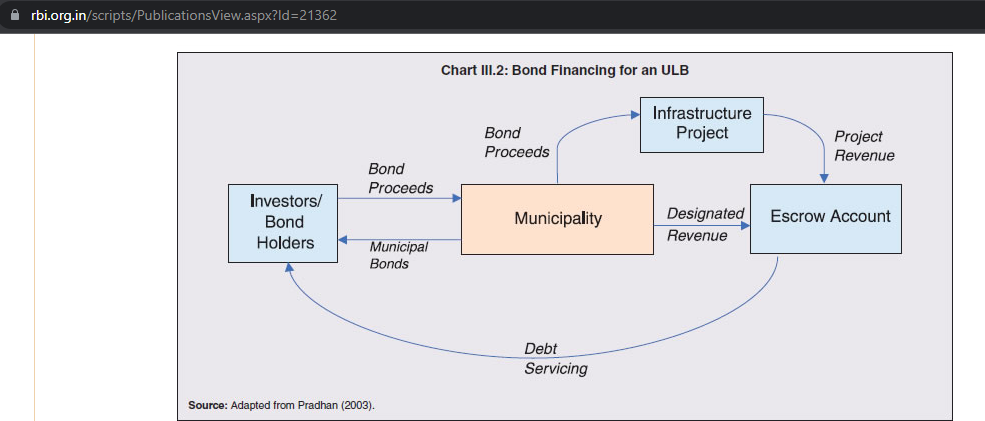
Understanding Municipal Bonds
As per the Reserve Bank of India’s guidelines, ULBs, local governments, and municipal authorities can issue bonds to investors in the secondary market to fund capital projects. Infrastructure projects include the development of schools, roads, bridges, flyovers, airports, public hospitals, etc.
The bond issuers, and government bodies, pay interest to bond investors at a particular coupon rate through the bond’s term and the entire principal on maturity. Bondholders enjoy a fixed interest rate and both short-term & long-term maturity periods from one to ten years. Retain investors can also enjoy tax exemptions in some instances.
Like corporate bonds, bond prices decline when market interest rates rise. Tax-exempt municipal bonds from government bodies with high credit ratings have almost zero credit risk. This makes a municipal bond an excellent bond investment for anyone.
How do Municipal Bonds work?
They are long-term debt instruments issued by a municipal corporation to acquire funds for public projects. A municipal bond belongs to the G-Sec category of tradeable instruments and is an ideal fixed-income security for investors as they carry almost no default risk.
What's the Minimum Amount You Need to Invest in Municipal Bonds?
Most municipal bonds require a minimum investment of Rs. 10000.
What Are Term Lengths Available for Municipal Bonds?
Short-term municipal bonds have a lock-in period of one year and mature in 3 years. Long-term bonds come with maturity periods of around 10 years.
Where can Investors find Information about Municipal Bonds?
Brokerage firms, online trading & investment platforms, banks, and government publications can offer accurate information regarding many municipal bonds.
What are the Factors you should Consider when Investing in Municipal Bonds?
Tax implications
In India, investors can enjoy tax exemptions if they meet specific criteria. Go through all terms, conditions, and constraints to determine whether you can avail of tax benefits.
Broker compensation
If you buy bonds through a brokerage firm, a broker will exact a commission at a specific rate. Rates vary across different firms.
SEBI Guidelines for Municipal Bonds in India
The Securities and Exchanges Board of India has certain eligibility conditions for the public issuance of any municipal bond.
- The issuing municipal body must have surplus income in the three years preceding the bond’s issuance. In addition, they must not have had a negative net worth in those three years.
- The issuer’s credit rating must be high, and they must not appear in the Reserve Bank of India’s wilful defaulter’s list.
- They must not have defaulted in making any payments to any financial institutions.
Municipal Bond Rates
The average coupon rate of a municipal bond in India ranges between 8% to 9%. (8.1% in 2021)
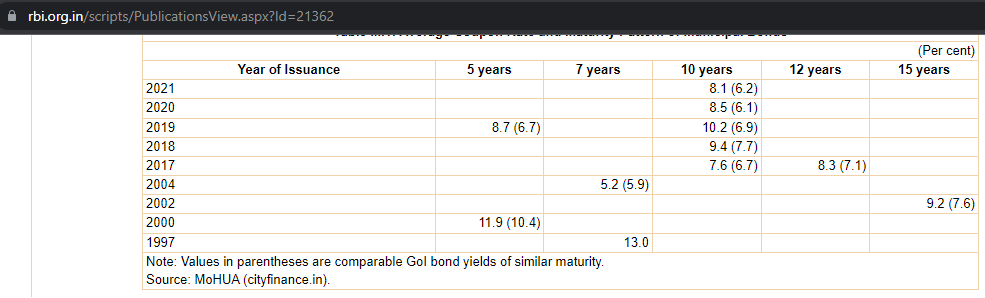
Backed by government entities, muni bonds come with almost no default risk, making them one of the safest investments for portfolio diversification.
Bengaluru, Ahmedabad, Indore, Lucknow, Vishakhapatnam, Nagpur, Nashik, Ghaziabad, Chennai, Surat, Ludhiana, Bhopal, Hyderabad, Madurai, Pune –these are some prominent cities that have issued debt instruments to acquire funds from the capital market.
You should buy municipal bonds as they promise decent interest payments., assure zero default risks, and also offer tax exemptions.
According to the RBI, the average interest rate is 8% to 9%. (8.1% in 2021 for a municipal bond with a 10-year maturity period)
According to the RBI, the average interest rate is 8% to 9%. (8.1% in 2021 for a municipal bond with a 10-year maturity period)
Anyone can invest in a municipal bond through a brokerage firm, online investment platforms, banks, or in some cases, directly through a municipality.
Inflation and tanking market rates are two main causes that can lead to some losses.